If you have knee pain from a bakers cyst, Chiropractic can provide relief! This post is about Knee Bursitis and Chiropractic Treatment: Baker’s Cyst.
What is bursitis?
Bursae are fluid-filled, sac like cavities. Bursae are located where muscles and tendons move over bony joint areas. They reduce friction caused by muscles and tendons moving against skin and bones. Also, they facilitate movement.
A knee bursa is like a cushion. So when one becomes inflamed, increased tension and pain can occur in a condition known as bursitis. The bursa in the knee increases with fluid and redness in the area occurs.
Symptoms and Signs of a Baker’s Cyst
You may have swelling, aching and tenderness in the popliteal area of the knee. The sac is located in the medial (inner) side of the popliteal fossa (diamond-shaped space behind the knee joint).
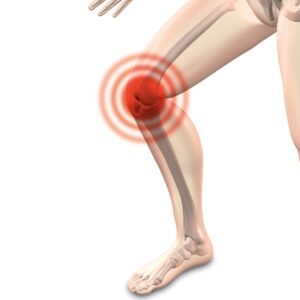
The Baker’s Cyst
The baker’s cyst is an idiopathic (cause unknown) form of bursitis where the cyst contents are not in the knee joint.
It can be found in children between ages 6-8 and 12-14 following rapid growth. Baker’s cysts in children are painless and normally disappear as the child matures.
In contrast, a baker’s cyst found in adults is symptomatic. In adults it has intra-articular (within joint) problems such as degeneration of posterior horn of the medial meniscus (C-shaped cartilage between shin bone and thigh bone) or synovial membrane (connective tissue joint lining) irritation.
Apparently, a baker’s cyst is due to swelling of the semimembranosus bursa. The semimembranosus bursa is located between the semimembranosus (one of a group of muscles called the Hamstrings) and gastrocnemius (calf muscle) tendon. Therefore, it is also called semimembranosus bursitis. Interestingly, poor flexibility of the semimembranosus and gastrocnemius muscles could contribute to development of a baker’s cyst. And this results in tendinitis.
Furthermore, degenerative joint disease or a torn meniscus are other possible contributing causes for a baker’s cyst.
Treatment for a Baker’s Cyst at Meiri Chiropractic
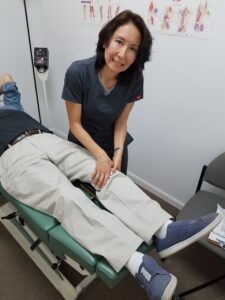
First, Chiropractic care for the knee conditions (e.g. tendinitis) can resolve the cyst.
Second, chiropractic manipulative therapy (adjustments) is rendered to the knee and associated spine and extremity (limb) joints.
Third, manipulation of muscle contractures with soft tissue techniques is utilized. Some Techniques include gentle PNF/PIR (e.g. post isometric relaxation) and/or myofascial release techniques.
Finally, therapeutic exercises for rehabilitation/ strengthening are prescribed. Especially, the lack of flexibility in the hamstrings and gastrocnemius are addressed.
Getting regular chiropractic treatment at a chiropractic center in West Palm Beach can help naturally relieve the pain and dysfunction of the knee. Chiropractic is a holistic and natural way to not only treat existing conditions, but to keep your body in its best working condition.
Contact Meiri Chiropractic today at 561-253-8984 to make an appointment or to learn more about Knee Bursitis and Chiropractic Treatment: Baker’s Cyst.