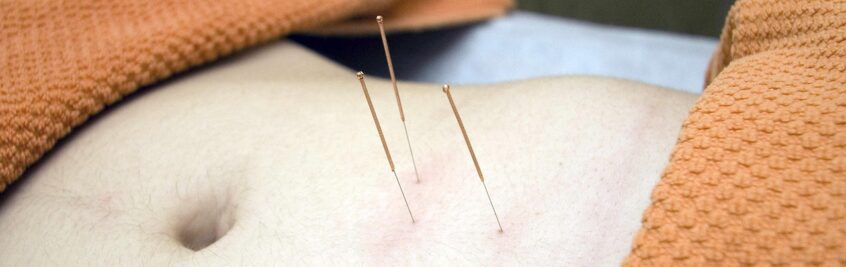
This post is about Chiropractor West Palm Beach: Acupuncture Helps Headaches. On the basis of the existing evidence, acupuncture can be a helpful complementary treatment for headaches. This is particularly true for migraines and tension-type headaches.
Studies suggest acupuncture can reduce the frequency and severity of headaches, and may offer longer-lasting relief than some medications. It’s also safe and cost effective. Lastly, it doesn’t have the side effects as some medications do. While not a cure, it can be a valuable option for those seeking alternatives or in conjunction with their headache management.
Causes of Migraines/Headaches: Neurologic Event
Firstly, Migraine is a common neurological disease. It is characterized by an unilateral (one sided), throbbing recurrent headache. Frequently, it is accompanied by photophobia (sensitivity to light), phonophobia (sensitivity to sound), or nausea.
Secondly, a neurologic event apparently occurs associated with an imbalance of serotonin during headaches. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that works with bodily functions. This includes mood, sleep, appetite, anxiety, digestion, and sexual desire. So too little or too much serotonin may contribute to headaches. And it matters where it occurs. Typically, too little serotonin in your central nervous system is the primary cause of headaches.
Thirdly, increased local vascular concentrations of serotonin may be part of an inflammatory cascade. These inflammatory chemicals include substance P. Substance P is a neurotransmitter found in the brain and spinal cord. It plays a role in transmitting pain signals. Ultimately, a neurogenic (originating from nervous system) vascular inflammation results. Truly, there are numerous chemical reactions causing headaches.

Causes of Headaches: Dopamine
Additionally, Scientist looked at the relationship between dopamine and migraine. And Dopamine is a neurotransmitter. This is a chemical messenger in the brain. Moreover, it plays a crucial role in bodily functions: reward system, movement, attention and focus, mood.
In one study, they assumed that depression and pain is caused by an imbalance or a deficiency of neurotransmitters (serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine). Also, they found long-term relief for chronic headaches. In conclusion, acupuncture treatments can trigger the release of endorphins such as dopamine. Endorphins are natural, feel-good chemicals produced by the body. They act as natural painkillers and mood enhancers.
Acupuncture Treatment for Migraines
Acupuncture improves blood flow and calms the nervous system. Researchers believe when an acupuncture needle is inserted, the sensory and proprioceptive nerves are stimulated. This sends a message to our brain and nervous system.
Our body’s enkephalins and endorphins are released. These are our body’s natural opioids and can dramatically relieve pain. Additionally, once these neurotransmitters are moving about, our blood vessels vasodilates. And this gets blood into the affected areas, initiating healing.
Recently, a team of researchers led by neuroscientists at Harvard Medical School has looked at the underlying neuroanatomy of acupuncture that activates a specific signaling pathway. In this study, they specifically investigated acupuncture as a potential treatment for inflammation. They found “acupoints” or acupuncture points on the body’s surface are mechanically stimulated, triggering nerve signaling that affects the function of other parts of the body, including organs.

Chiropractor West Palm Beach: Acupuncture Helps Headaches
Acupuncture has been used for over 4000 years to treat pain and other health problems. The acupuncture treatment stimulates the imbalanced meridian pathways to bring balance back. This activates the body’s natural healing abilities. It’s often used as part of a broader approach to healthcare. Indeed, Acupuncture has a beneficial effect when treating many diseases and painful conditions.
Meiri Chiropractic offers acupuncture for headaches and many other ailments. Dr. Natalie Meiri is a chiropractic physician, board certified in acupuncture with over 20 years of experience. Call today for your acupuncture treatment for headaches at 561-253-8984.
References: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7606388/

 i
i